Imagine: It’s 9 PM on a Friday and Maria, a finance manager for a midsize travel agency in Mumbai, is still at her desk. She compares 1,247 bookings out of their GDS against bank statements containing payments amounting to 1,193 and supplier invoices that somehow add up to something completely different amount. Three screens are lit with Excel sheets, each of which holds parts to a financial puzzle that should come together seamlessly but doesn’t. This is happening every day in thousands of travel agencies all over the world.
Booking reconciliation has become the quiet productivity killer in travel. With agencies investing in providing great customer experiences and growing their service offering, the back-office administration of reconciling bookings to payment can tie up valuable staff time. Phocuswright reported that travel agencies spend 15-20% of their operational time on reconciliation but continue to suffer from sub-85% accuracy scores.
In this exhaustive guide, we’ll take a close look at what booking reconciliation really means for travel agencies; why it is still tediously time-consuming despite the advances in technology; and most importantly, how you can use your approach to booking reconciliation to turn hours of necessary standalone tasks into a cumbersome but efficient part of your process that actually adds value to your business.
Booking Reconciliation is the crucial function of confirming and reconciling all financial details on travel bookings in various systems to guarantee that customer bookings, payment history, supplier invoices and any commission remunerations are aligned. It’s like conducting a financial orchestra where every instrument your GDS, payment gateway, accounting software and supplier portals all have to keep time together.
There are three critical data streams that intercross and process in perfect synchronization. First the booking data comes from multiple sources, including GDS booking platforms such as Amadeus (which handles over 1.9 billion transactions each year according to their 2023 annual report), Sabre and Travelport as well as from direct supplier links and online booking tools. Every reservation has dozens of points of data: passenger names, PNRs, date of travel, fare components, taxes and service fees.
Second, payment data comes through a variety of channels credit card processors, bank transfers, mobile payment apps, and cash payments. According to data from the World Travel & Tourism Council, the global travel payments market was valued at approximately $1.4 trillion in 2023, and agencies have had to deal with the increasing complexity of payment scenarios such as partial payments, multi-currency transactions and dynamic currency conversions.
Third, there is also supplier invoicing on top of that. Indeed, airlines, hotels, car rental companies and tour operators all have different invoicing cycles, commission structures and payment terms. For one booking you could have five different suppliers issuing invoices, all with different billing dates and formats as well as reference systems.
The reconciliation process follows a structured workflow that, while logical in theory, becomes incredibly complex in practice:
Data Extraction and Normalization: This is basically the process of obtaining data from different systems and transforming all the information to match one another. This seemingly straightforward action is often more complicated, as you need to extract the numbers from what may look like “AA-789456” in your GDS but might be “789456-AA-2024” in the airline’s system.
Automated Matching and Validation, it tries to match notes based on booking references, passenger name, travel date and amount. Indeed, according to McKinsey we have often seen that automated matching has had only been able to do 60-70% of matches successfully for travel due to data mismatches, and there is excessive manual work.
Exception Management detects mismatches, from the simplest things like typos to more sophisticated cases such as split payment over multiple cards or bookings that are partially refunded due to time-of-travel changes.
Resolution and Reporting document, resolves and adjusts processes with the drilling units and maintains accurate financial recordkeeping for purposes of accounting, tax compliance and management reporting.
Even in the era of AI and automation, travel payment reconciliation remains surprisingly manual and resource intensive. Insight into these struggles explains why so many firms continue to assign entire teams to the role.
Travel agencies rely on a patchwork of disconnected systems that were not built to talk to one another. Phocuswright research suggests that most travel agencies have 7-12 independent software suites in use which are not natively integrated. Your GDS speaks one language, your accounting system another, and your payment gateway one more. Every time the system is updated, we are at risk that existing integrations are severed, and manual processing required.
Imagine a standard booking flow: A reservation comes in from Amadeus; payment goes through Stripe or Adyen; the invoice is received via an email generated by the airline; everything has to be reconciled in QuickBooks or SAP. A handoff point is a place where problems, delays and differences are introduced.
When automated connections don’t work occurring more frequently than vendors are willing to acknowledge staff members have to transfer the data between systems by manually. According to a study conducted by the University of Hawaii, manual data entry is subject to error rates ranging from 0.55% and 3.6% for each field. For an agency that handles 1,000 bookings every month and has to complete 20 fields of data for each booking, that equates to 110-720 errors before anything else.
These errors compound exponentially. Payment can’t be automatically matched due to a transposed digit in the booking reference. The exemption is up for manual review, which can be full of exhausted employees making further mistakes or failing to also pay attention to related problems. This lighthearted mistake turns into hours of digging through code and updating notes.
The travel industry’s pricing complexity makes reconciliation exponentially harder than other industries. A single airline ticket might include:
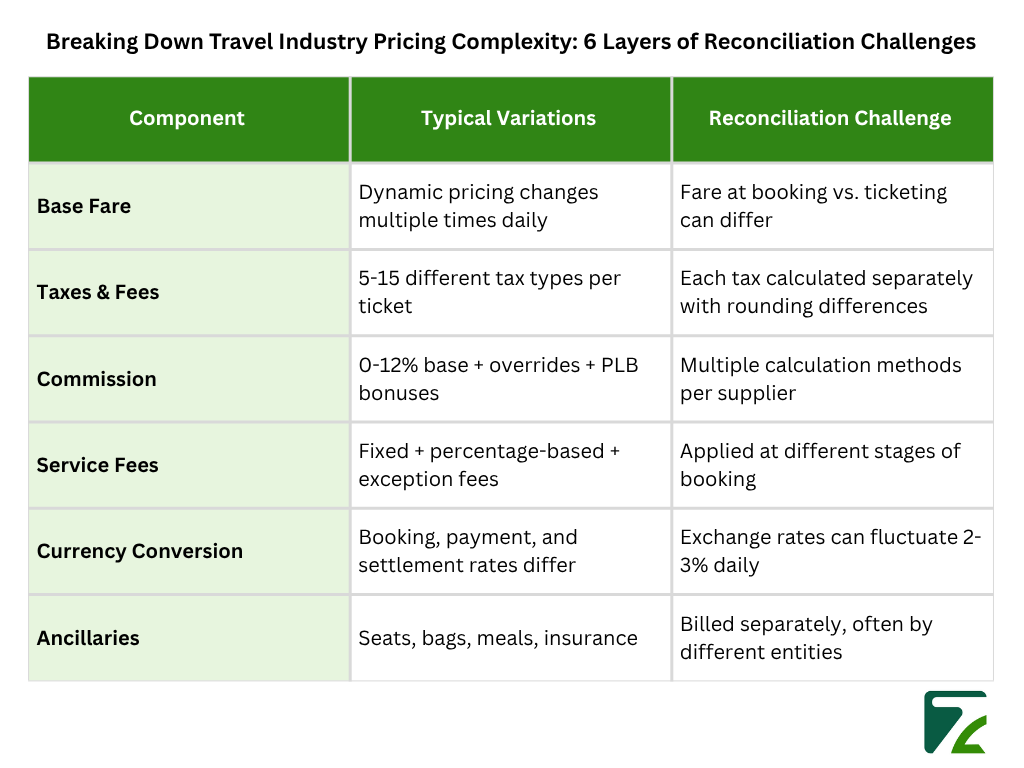
The number of transactions is simply too high for manual intervention. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) says that the airlines alone turnover more than 4 billion passenger journeys per annum for which travel agency transaction is also responsible for a major segment of the booking process. A mid-sized agency might process:
This results in thousands of data points that need to be reconciled on a daily basis, any one of which could fall out of sync as time passes.
Delayed reconciliation plays hard on visibility to cash flow. Agencies lack real-time reconciliation, and work with outdated financial data to run the business and make mission-critical decisions on incomplete information. McKinsey’s working capital benchmarking reveals firms with their reconciliation in check can benefit from 15-20% improvement on working capital.
Unreconciled commissions represent lost revenue. ASTA (American Society of Travel Advisors) industry estimates are that 2-4% in earned commissions is not collected by agencies as a result of these reconciliation gaps for an agency with $10 million per year in revenue, that equals $200,000-$400,000 lost income every year.
Reconciliation delays strain supplier relationships. Addressing discrepancies weeks or months after they emerge is then an order of magnitude more difficult. Suppliers may have closed their books; staff may have turned over and supporting documentation can get archived or lost. According to the Airlines Reporting Corporation (ARC), 68% of debit memos would be eliminated with prompt settlement.
Delays in payment due to reconciliation glitches can put preferred supplier agreements, override commissions, and negotiated rates at risk. In a world in which average margins to the travel agency sector are barely above 8-12% (according to Travel Weekly’s Agency Survey), preserving these preferred arrangements is critical for profitability.
Agencies are evolving how they reconcile bookings with the help of artificial intelligence. The state-of-the-art AI systems of today don’t just match data, they learn from patterns, anticipate problems and constantly improve accuracy. Juniper Research says that artificial intelligence in travel will save the industry $16.8 billion a year by 2025.
RPA bots are also able to perform repetitive reconciliation duties 24/7, non-stop without tiredness or mistakes. RPA can cut the processing time of reconciliations by 80% and increase the accuracy up to 99.9%, according to Deloitte’s RPA survey. These bots can:
Today’s integration platforms can break down these data silos by providing connectivity between systems in real-time. Gartner’s integration platform indicates that organizations are reducing the cost of integration by 65% with iPaaS (integration platform-as-a-service) solutions. These platforms offer:
The use of confirming data formats between all systems will result in a vast increase in matching rates. Leverage industry standards such as IATA’s NDC (New Distribution Capability) are widely used by over 100 airlines worldwide for uniform data interchange. Institute standard naming conventions for booking references, passenger names and payment descriptions.
Develop structured flows for different exception categories:
Monthly reconciliation audits scheduled to spot ongoing problems and process holes. Monitor vital metrics such as first-time match rates, average resolution time, exception volumes by type and root cause analysis of mismatches. Leverage this information to further refine matching rules and processes.
In order to measure reconciliation efficiency, you must manage a set of objective KPIs that demonstrate clear operational efficiency and financial accuracy:
As you assess reconciliation technology for your travel agency, think about these key criteria:
Your reconciliation program has to be able to communicate with existing systems easily. Find pre-built connectors to popular GDS platforms (Amadeus, Sabre, Travelport), payment service providers and accounting tools. API flexibility is key , REST has emerged as the established standard for modern integrations.
As your agency scales, so should your reconciliation systems. Compared to on-premises, Cloud solutions are much more scalable. “As per AWS’s travel insights, cloud-based travel platforms can scale to handle 10x transaction volumes without infrastructure .
Comprehensive reporting capabilities are non-negotiable. Your system should be able to give you dashboards in real-time, enable you to drill down capabilities, and offer alerts for exceptions; they must also provide custom reports. Tableau and Power BI are great too for reconciliation type data visualization.
Booking reconciliation doesn’t have to be the heavyweight that destroys your finance team’s evenings. In understanding why reconciliation is inherently difficult in travel, recognizing the true cost of manual processing and embracing today’s technological advances, agencies can turn what has always been a necessary evil into a differentiator.
The transition from a manual Excel-based reconciliation process to an automated, AI-driven one isn’t just about saving time–it’s also about enhancing accuracy and recovering lost revenue all while providing real-time financial visibility to drive better business decisions. Firms that can effectively reconcile their payments get certain cold hard benefits in an industry with tight margins and lots of competition.
It’s not just the numbers: agencies utilizing automated reconciliation systems see a 75% decrease in processing time, accuracy is at approximately 99% versus manual processes (previously only around 85%), aged receivables are down by roughly 95%, and overall additional commission income is recovered at a rate of 2-4%. These enhancements all have a positive impact on profitability and market competitiveness.
Begin by comparing your current reconciliation process with the KPI benchmarks profiled in this guide. Map out your largest pain points, data silos, manual processes, exception handling and score action items high or low impact to gauge what you can do with a reasonable amount of effort. It is important to note that even marginal gains of reconciliation efficiency can result in substantial financial returns.
The steps to proceed for travel agencies who want to become smarter about reconciliation are obvious: standardize your data, automate the no-brainer matching, consider smart exception handling and always measure and grow your processes. Investing in better reconciliation is not just about cost savings, it’s also about building a more streamlined, profitable, scalable travel business.
Booking reconciliation is the process of matching bookings, payments, supplier invoices, and commissions to ensure financial accuracy. It’s crucial because errors directly affect cash flow, profitability, and supplier relationships.
They compare booking data from GDS/booking tools with payment gateways, bank statements, and supplier invoices. Commissions are verified against agreed rates. Often, automation or accounting software is used, but manual checks are still common.
Frequent issues include mismatched data formats, manual entry errors, multiple currencies, partial payments, and different supplier billing cycles making the process time-consuming and error-prone.
Agencies can use AI-driven platforms, robotic process automation (RPA), and cloud-based integrations that connect GDS, payment gateways, and accounting software.
Delays can block cash flow visibility, lead to unclaimed commissions (2–4% of revenue), cause supplier disputes, and increase write-offs. Automating reconciliation can recover revenue and improve working capital by 15–20%.

Travel Automation Expert