Outsourcing vs Offshoring: Understanding the Differences, Benefits, and Strategic Choices
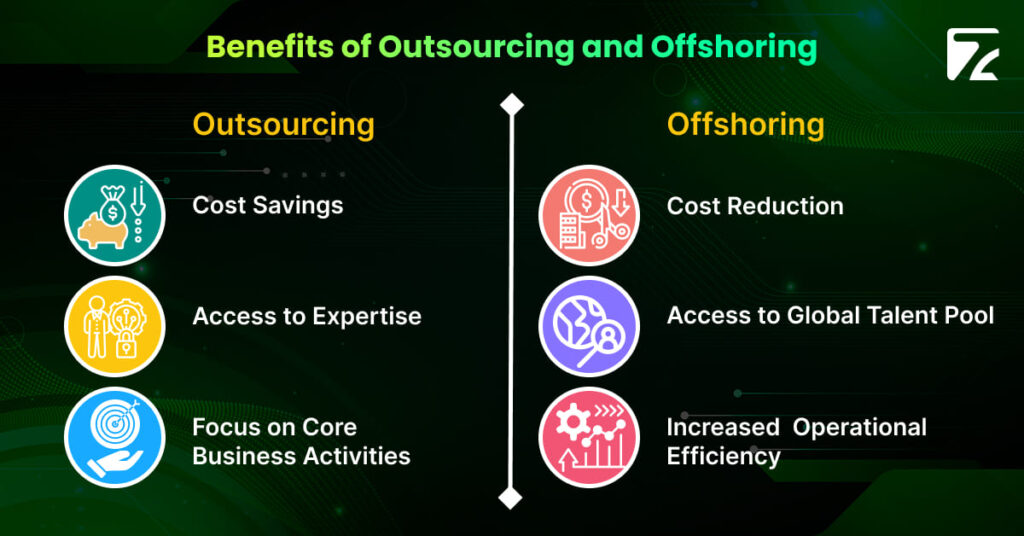
Outsourcing vs Offshoring: Understanding the Differences, Benefits, and Strategic Choices [boomdevs_toc] In our globalized economy, businesses are constantly looking for ways to boost efficiency and cut costs. Outsourcing and offshoring are two popular strategies to achieve these goals. Although they might seem similar, they have unique differences and benefits that can greatly influence a company’s operations. Understanding these concepts is key to making smart business choices. Additionally, these approaches can enhance competitiveness, drive innovation, and provide access to specialized skills and technologies. As companies operate in an increasingly connected world, grasping the distinctions between outsourcing and offshoring is vital for making the best use of resources and ensuring long-term success. Understanding Outsourcing History and Evolution of Outsourcing To begin with, outsourcing has a rich history that dates back to the late 20th century. Initially, businesses started outsourcing non-core functions such as payroll and customer service to external providers. Over the years, the scope of outsourcing has expanded significantly, encompassing a wide range of services from IT to human resources. This evolution has been driven by the need for businesses to focus on core activities while leveraging external expertise. Key Drivers of Outsourcing Furthermore, several key drivers propel the decision to outsource. Primarily, cost savings are a major incentive. By outsourcing, companies can reduce labor costs, overhead expenses, and avoid significant capital investments in infrastructure. Additionally, outsourcing offers access to specialized skills that may not be available in-house, allowing businesses to leverage external expertise to enhance their operations. Industries that Use Outsourcing Moreover, outsourcing is prevalent across various industries. Sectors such as information technology, customer service, healthcare, and manufacturing commonly utilize outsourcing to gain competitive advantages. These industries benefit from the expertise, efficiency, and cost savings provided by third-party service providers. Understanding Offshoring History and Evolution of Offshoring Similarly, offshoring has gained momentum alongside globalization. Initially, it involved relocating manufacturing operations to countries with lower labor costs. Today, offshoring encompasses a broader range of functions, including software development, research, and back-office operations. This strategy enables companies to tap into the global talent pool and achieve substantial cost savings. Key Drivers of Offshoring The key drivers of offshoring are quite compelling. Firstly, significant cost reduction is a primary factor. By relocating operations to countries with lower labor costs, companies can achieve substantial savings. Secondly, offshoring provides access to a diverse global talent pool, allowing businesses to leverage specialized skills and expertise available in different regions. Lastly, increased operational efficiency is another advantage, as companies can operate around the clock due to different time zones. Common Industries that Utilize Offshoring Offshoring is particularly beneficial for industries such as technology, finance, pharmaceuticals, and customer service. These sectors can take advantage of the cost savings, expertise, and efficiency gains available in various global markets. Benefits of Outsourcing Cost Savings One of the most significant benefits of outsourcing is cost savings. By contracting out non-core functions, companies can reduce labor costs and overhead expenses. This enables businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and focus on their core activities. Access to Expertise Additionally, outsourcing provides access to specialized expertise that may not be available in-house. This allows companies to leverage the skills and knowledge of professionals who are experts in their respective fields, enhancing the quality and efficiency of their operations. Focus on Core Business Activities Moreover, by outsourcing non-core functions, companies can concentrate on their core business activities. This focus enhances efficiency and allows the organization to concentrate on strategic growth and development. Benefits of Offshoring Cost Reduction Offshoring offers substantial cost reductions, particularly in labor-intensive industries. By relocating operations to countries with lower labor costs, companies can achieve significant savings and improve their bottom line. Access to Global Talent Pool Furthermore, offshoring provides access to a diverse global talent pool. This allows companies to tap into specialized skills and expertise available in different regions, fostering innovation and productivity. Increased Operational Efficiency In addition, offshoring certain functions can increase operational efficiency. Companies can streamline processes, access advanced technology, and operate around the clock due to different time zones, enhancing overall productivity. Challenges of Outsourcing Quality Control Issues Despite the numerous benefits, outsourcing comes with challenges. One major issue is maintaining quality control. Ensuring that third-party providers meet the required standards can be difficult, potentially leading to issues with product or service quality. Communication Barriers Communication barriers can also arise when outsourcing to providers in different regions. Differences in language, time zones, and cultural norms can complicate coordination and collaboration, affecting overall efficiency. Dependency on Third Parties Additionally, relying on third-party providers can create dependencies that may pose risks. If the provider fails to deliver, it can disrupt business operations and impact overall performance. Challenges of Offshoring Cultural Differences Offshoring also presents its own set of challenges, particularly when it comes to fostering an inclusive work environment across different regions. Cultural Differences can pose significant hurdles, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts arising from varying work cultures, communication styles, and business practices. Emphasizing Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) can help bridge these gaps by promoting respect and understanding among diverse teams, ensuring smoother collaboration and greater productivity.” Political and Economic Risks Moreover, offshoring carries political and economic risks. Changes in government policies, economic instability, and geopolitical tensions can impact operations in offshore locations, creating uncertainty and potential disruptions. Time Zone Differences Time zone differences can create challenges in coordination and communication. While operating around the clock can be an advantage, it also requires effective management to ensure seamless collaboration and avoid delays. Outsourcing vs Offshoring: A Comparative Analysis Cost Implications When comparing outsourcing and offshoring, cost implications are a crucial factor. Both strategies offer cost benefits, but the extent varies. Outsourcing typically provides immediate cost savings in specific functions, while offshoring offers broader cost reductions across various operations. Quality and Control Quality and control are also important considerations. Outsourcing can pose quality control challenges due to reliance on third-party providers. On the other hand, offshoring can maintain better control over operations but may face cultural and management
